PDF] Compressive Ulnar Neuropathies at the Elbow: I. Etiology and
$ 13.99 · 5 (247) · In stock

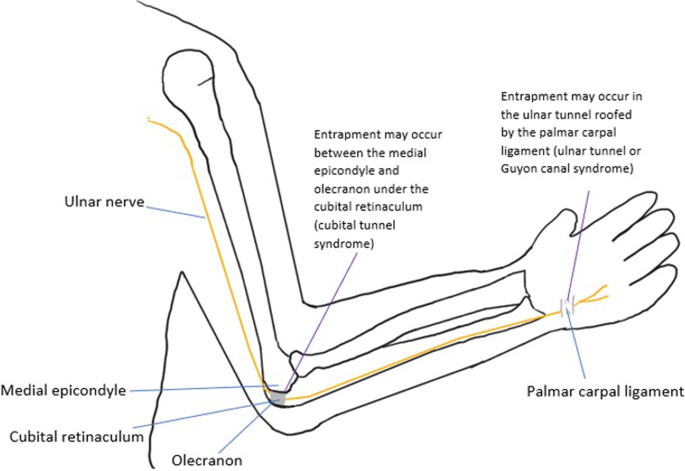
The differential diagnosis of ulnar neuropathies at the elbow includes lesions that cause additional proximal or distal nerve compression and systemic metabolic disorders. &NA; Ulnar nerve compression at the elbow can occur at any of five sites that begin proximally at the arcade of Struthers and end distally where the nerve exits the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle in the forearm. Compression occurs most commonly at two sites—the epicondylar groove and the point where the nerve passes between the two heads of the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle (i.e., the true cubital tunnel). The differential diagnosis of ulnar neuropathies at the elbow includes lesions that cause additional proximal or distal nerve compression and systemic metabolic disorders. A complete history and a thorough physical examination are essential first steps in establishing a correct diagnosis. Electrodiagnostic studies may be useful, especially when the site of compression cannot be determined by physical examination, when compression may be at multiple levels, and when there are systemic and metabolic problems.

PDF] Compressive Ulnar Neuropathies at the Elbow: I. Etiology and Diagnosis
Nerve entrapment syndromes of the upper limb: a pictorial review, Insights into Imaging

Cubital Tunnel Syndrome

Entrapment of the ulnar nerve in cubital tunnel by free intra-articular body—a case report - JSES Open Access
Ulnar claw - Wikipedia
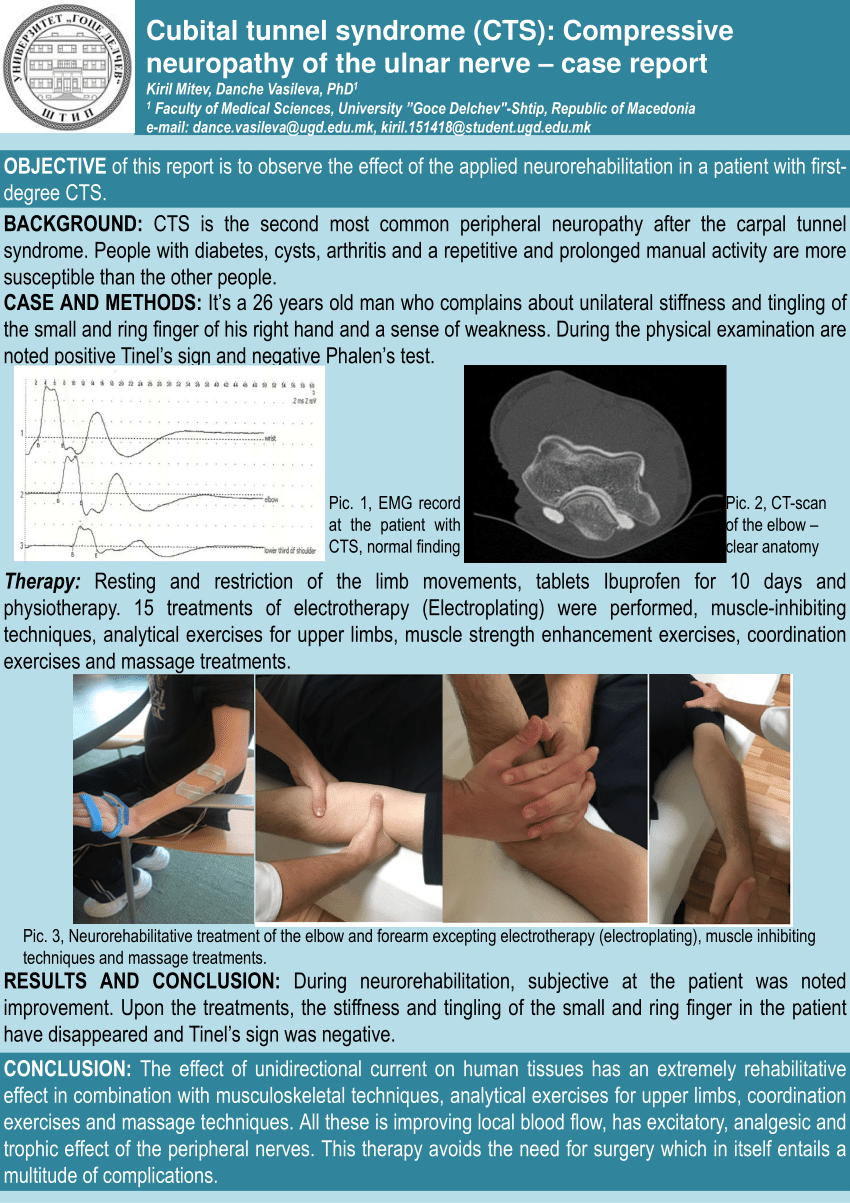
PDF) Cubital tunnel syndrome: Compressive neuropathy of the ulnar nerv - case report

PDF) Revision Decompression and Collagen Nerve Wrap for Recurrent and Persistent Compression Neuropathies of the Upper Extremity

Ulnar Neuritis Information Florida Orthopaedic Institute

PDF) Recalcitrant cubital tunnel syndrome Plastic and Aesthetic Research