Associations of body shapes with insulin resistance and
$ 18.50 · 4.9 (86) · In stock
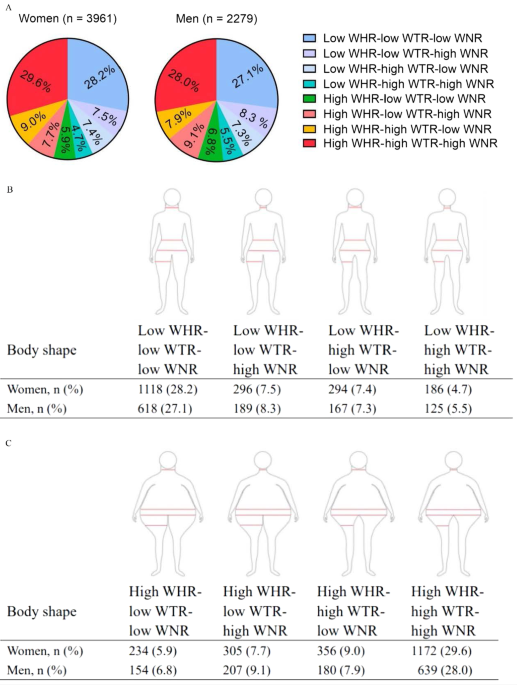
Background We aimed to define refined body shapes by using multiple anthropometric traits that represent fat distribution, and evaluate their associations with risk of insulin resistance (IR) and cardiometabolic disorders in a Chinese population. Methods We performed a cross-sectional analysis in 6570 community-based participants aged ≥ 40 years. Four body circumferences (neck, waist, hip, and thigh) and their ratios were put simultaneously into an open-source Waikato Environment for Knowledge Analysis platform to select the worthiest indicators in determining IR. The ratio of the top 3 fat distribution indicators was used to define the refined body shapes. Results We defined 8 distinct body shapes based on sex-specific combinations of waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), waist-to-thigh ratio (WTR), and waist-to-neck ratio (WNR), which differed in participants’ distribution and risk of IR and related cardiometabolic disorders. In women, as compared to the low WHR-low WTR-low WNR shape, all body shapes were significantly associated with IR and related cardiometabolic disorders; while in men, the low WHR-high WTR-high WNR shape and the higher WHR related shapes were significantly associated with IR and related cardiometabolic disorders. Stratified by WHR, the results were consistent in women; however, no significant associations were detected in men. Conclusions We defined 8 distinct body shapes by taking WHR, WTR, and WNR, simultaneously into account, which differed in association with the risk of IR and related cardiometabolic disorders in women. This study suggests that body shapes defined by multiple anthropometric traits could provide a useful, convenient, and easily available method for identifying cardiometabolic risk.

PDF) The role of insulin resistance in the relation of visceral, abdominal subcutaneous and total body fat to cardiovascular function
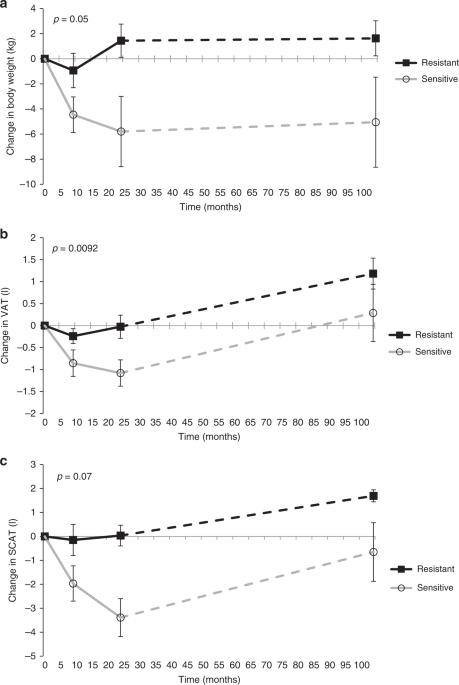
Brain insulin sensitivity is linked to adiposity and body fat distribution

The Link Between PCOS and Diabetes

Yuhong Chen's research works Ruijin Hospital North, Shanghai and other places

Association of changes in PA levels and insulin sensitivity, body

Associations of body shape index (ABSI) and hip index with liver, metabolic, and inflammatory biomarkers in the UK Biobank cohort
Mid-Arm Circumference and All-Cause, Cardiovascular, and Cancer Mortality among Obese and Non-Obese US Adults: the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey III

Mean ( Ȁ SE) differences in the cross-sectional abdominal body shape

Flow chart of the recruitment and selection procedure of the study

Causal associations between cardiorespiratory fitness and type 2 diabetes

Association between obesity phenotypes of insulin resistance and risk of type 2 diabetes in African Americans: The Jackson Heart Study - ScienceDirect