Repressive elements co-evolve with splice site sequences at
$ 32.50 · 4.9 (256) · In stock
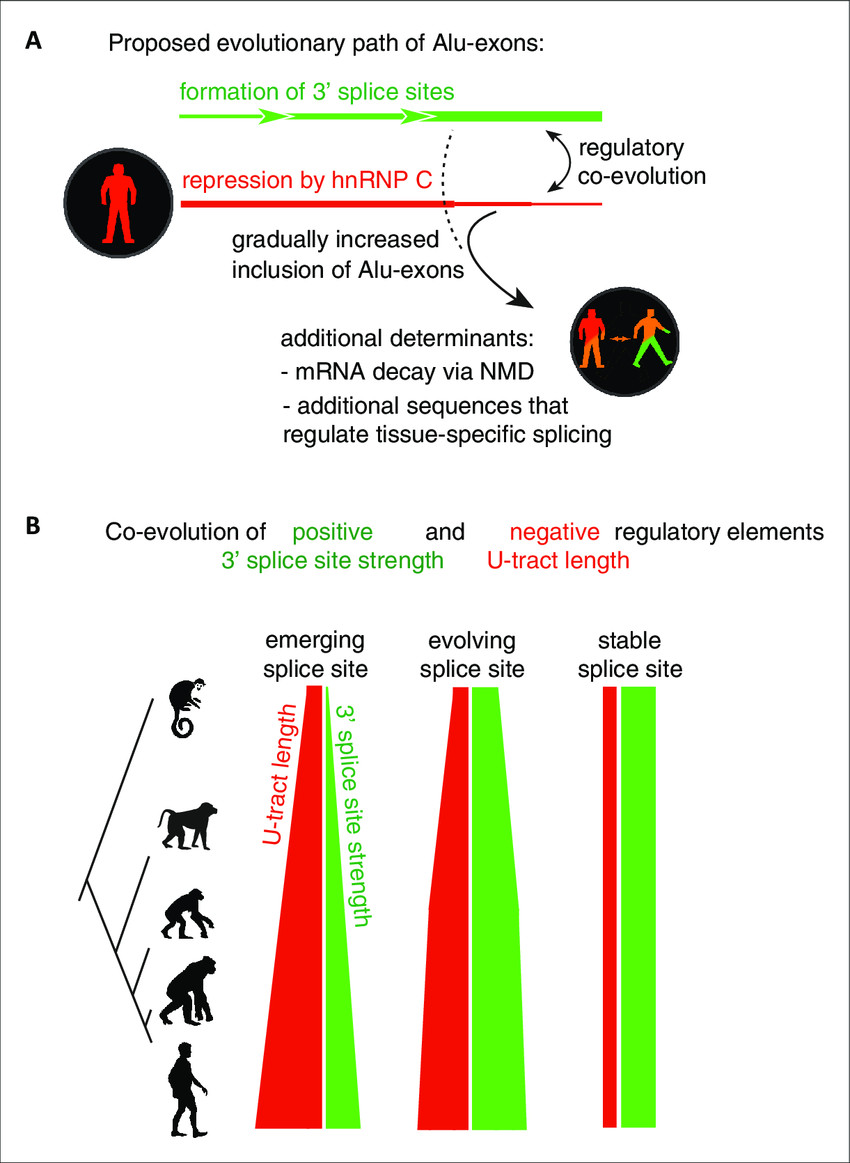

Evolution of intron–exon structures and alternative splicing of the 3′

Nejc HABERMAN, Imperial College Research Fellow, Doctor of Philosophy, Imperial College London, London, Imperial, Department of Brain Sciences

Analysis of the relation between ribosomal protein genes transcription
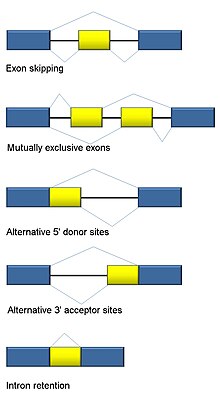
Alternative splicing - Wikipedia
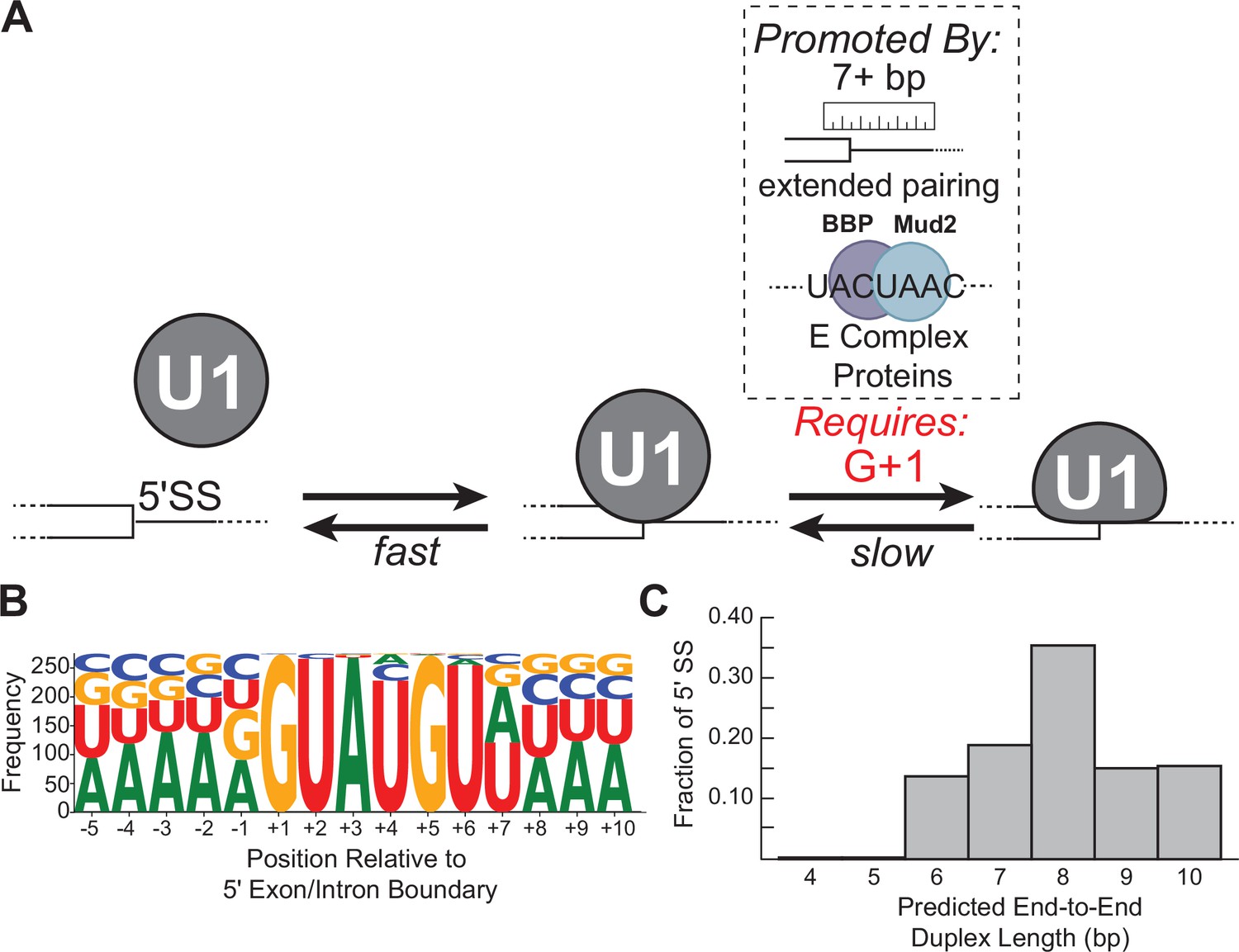
Multi-step recognition of potential 5' splice sites by the Saccharomyces cerevisiae U1 snRNP
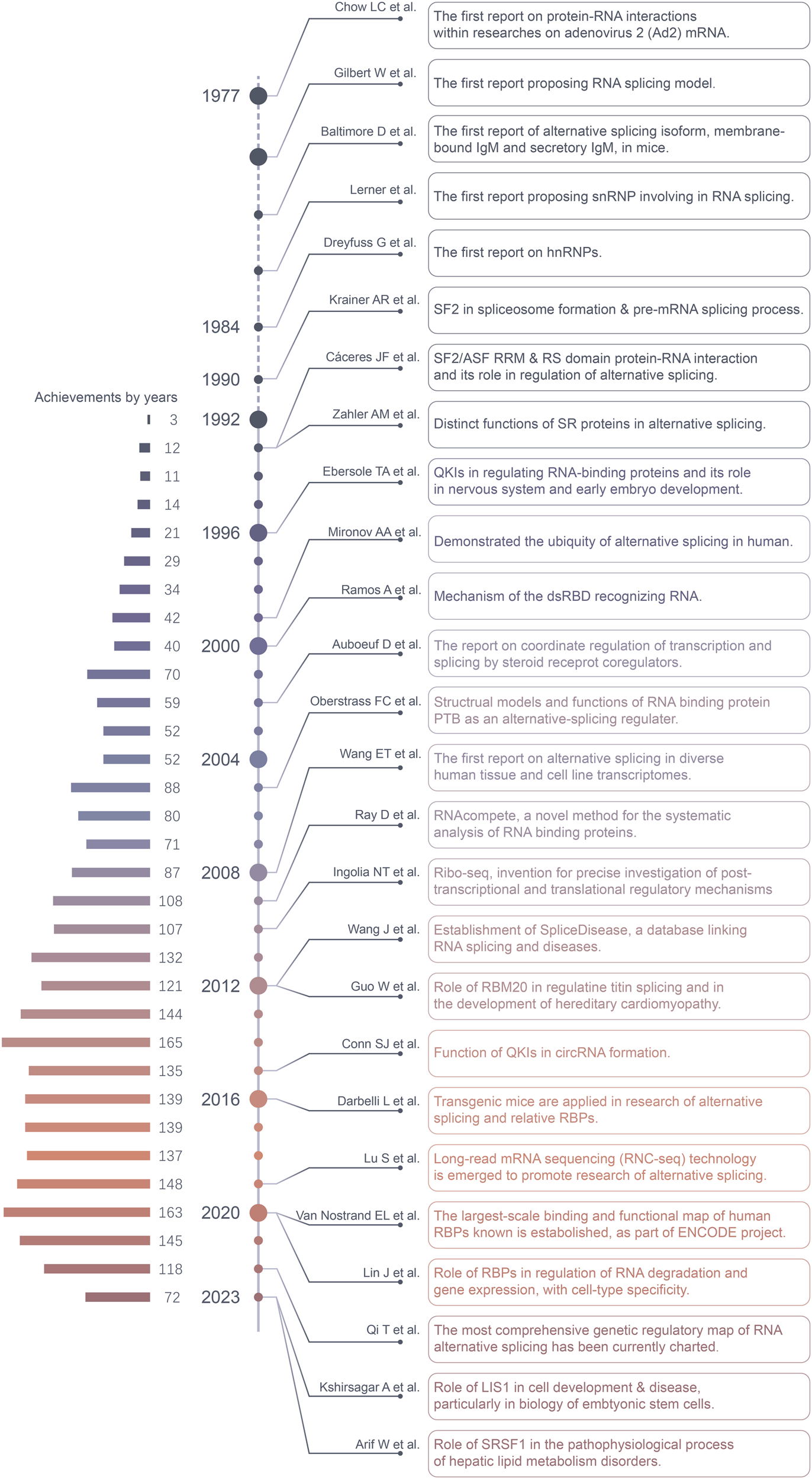
Alternative splicing and related RNA binding proteins in human

Repressive elements co-evolve with splice site sequences at cryptic
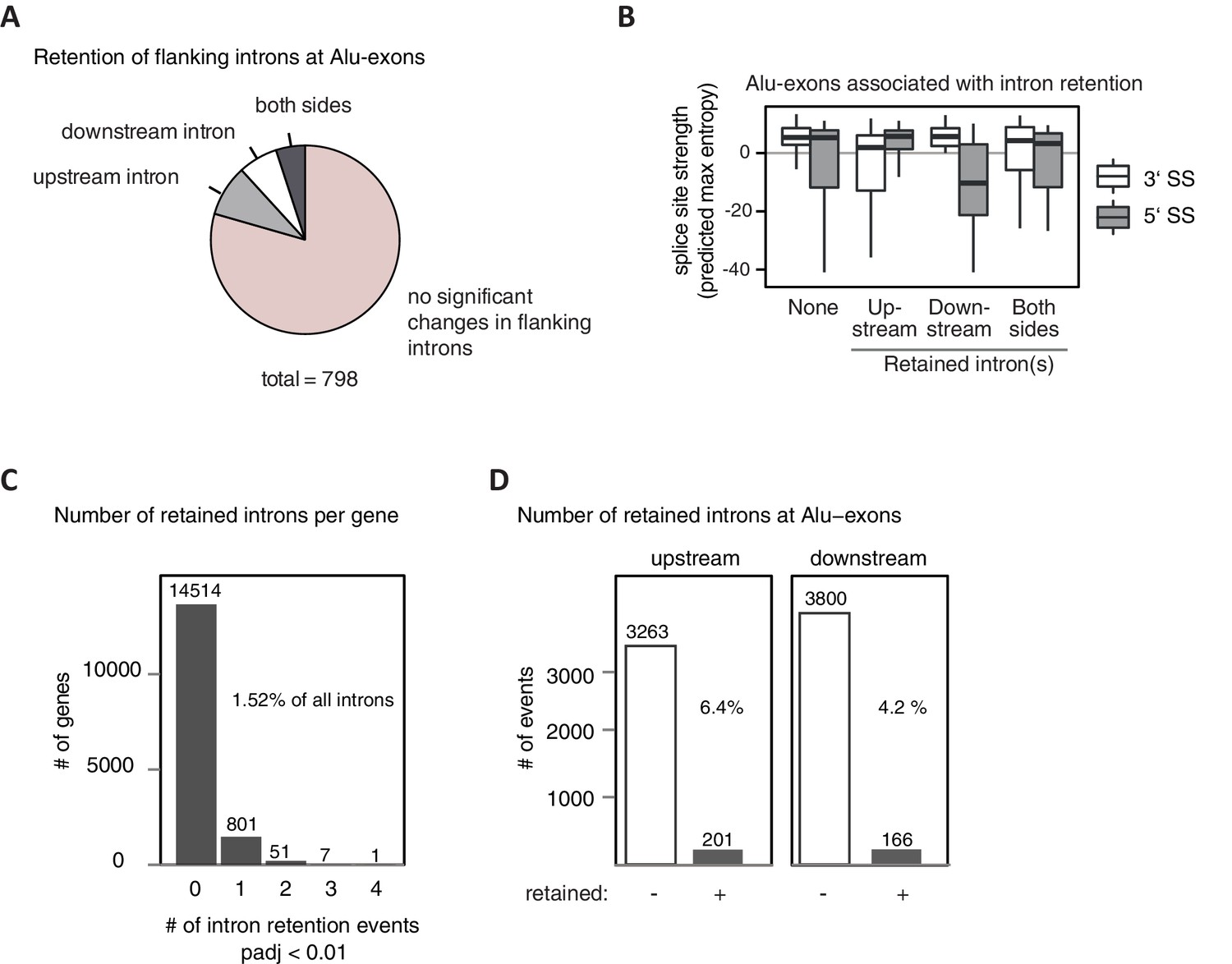
Splicing repression allows the gradual emergence of new Alu-exons in primate evolution

U1 snRNP partially rescue the ATT haplotype. (a) Schematic

Igor RUIZ DE LOS MOZOS, Computational Research Associate, PhD, The Francis Crick Institute, London, UCL Molecular Neuroscience

Transposable element-derived sequences in vertebrate development, Mobile DNA

Splicing repression allows the gradual emergence of new Alu-exons in primate evolution. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Alu-exons are a novel class of NMD substrates. (A) Depletion of

Alternative Splicing Regulatory Networks: Functions, Mechanisms, and Evolution - ScienceDirect