Response of granular anammox process under mainstream conditions to continuous and transient organic loads - ScienceDirect
$ 19.50 · 4.8 (211) · In stock


Characteristics and mechanism of anammox granular sludge with different granule size in high load and low rising velocity sewage treatment - ScienceDirect

Recovery of anammox process performance after substrate inhibition: Reactor performance, sludge morphology, and microbial community,Bioresource Technology - X-MOL

Response of granular anammox process under mainstream conditions to continuous and transient organic loads - ScienceDirect

Response of microbial succession of Anammox granular sludge (AnGS) and essential abundance under salty stress and temperature reduction - ScienceDirect
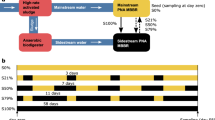
Temperature modulates stress response in mainstream anammox reactors

Characteristics of anammox granular sludge using color differentiation, and nitrogen removal performance of its immobilized fillers based on microbial succession - ScienceDirect

Simultaneous anammox-denitrification process and its emerging extensions - ScienceDirect

Improving mechanical stability of anammox granules with organic stress by limited filamentous bulking - ScienceDirect

Response of granular anammox process under mainstream conditions to continuous and transient organic loads - ScienceDirect

Insights on pretreatment technologies for partial nitrification/anammox processes: A critical review and future perspectives - ScienceDirect

Treating the filtrate of mainstream anaerobic membrane bioreactor with the pilot-scale sludge-type one-stage partial nitritation/anammox process operated from 25 to 15 °C - ScienceDirect

A critical review of improving mainstream anammox systems: Based on macroscopic process regulation and microscopic enhancement mechanisms - ScienceDirect

Characteristics and mechanism of anammox granular sludge with different granule size in high load and low rising velocity sewage treatment - ScienceDirect

PDF) Complete nitrogen removal from municipal wastewater via partial nitrification by appropriately alternating anoxic/aerobic conditions in a continuous plug-flow step feed process