Slip length and structure of liquid water flowing past atomistic smooth charged walls
$ 13.00 · 4.8 (482) · In stock

Slip length measurement in rectangular graphene nanochannels with a 3D flow analysis - ScienceDirect

Properties of Water from Numerical and Experimental Perspectives 0367138026, 9780367138028

Carbon nanotube membranes – Strategies and challenges towards scalable manufacturing and practical separation applications - ScienceDirect

Three-Dimensional Structure of a Simple Liquid at a Face-Centered-Cubic (001) Solid Surface Interface

Water in Nanopores and Biological Channels: A Molecular Simulation Perspective. - Abstract - Europe PMC
A, B) Average widths as a function of fabrication strain for (A)

Carbon nanotube membranes – Strategies and challenges towards scalable manufacturing and practical separation applications - ScienceDirect
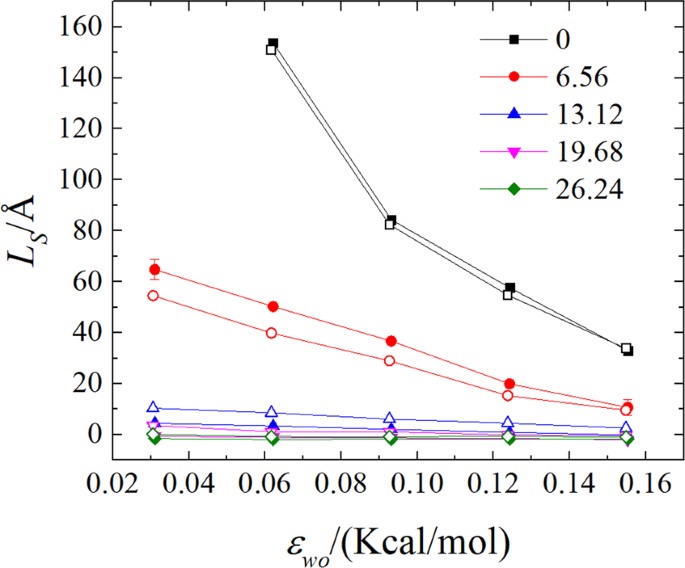
The influences of electric field intensity and driving force on the slip behaviour of water flow in a nanochannel

Viscosity ratios and slip length variations with the surface charge.

Water in Nanopores and Biological Channels: A Molecular Simulation Perspective. - Abstract - Europe PMC
Water Permeation Through a Charged Channel

A Model for Wall Slip Prediction of Confined n-Alkanes: Effect of Wall-Fluid Interaction Versus Fluid Resistance

Amontons-Coulomb-like slip dynamics in acousto-microfluidics

Pressure (P xx ) within the fluid confined in 15r m -width parallel

The simulation model of liquid water confined between two planar
